How IoT is Revolutionizing Hospitals: A Global Perspective on Patient Care and Operational Efficiency
Looking to modernize your Hospital, Lab or Clinic?
Hospi is trusted across 25 Indian states for billing, EMR, lab reports, automations & more.
Introduction
The healthcare industry is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by advancements in technology. Among these, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a game-changer, transforming hospital operations and patient care. Hospitals across the globe, from the United States to the United Kingdom, Australia, and India, are integrating IoT-driven solutions to enhance patient outcomes, streamline processes, and improve overall efficiency.
For hospital administrators, doctors, and decision-makers, understanding the significance of IoT is no longer optional—it is essential for staying competitive and delivering high-quality care. This article explores the role of IoT in modern hospitals, its key applications, benefits, challenges, and the future of IoT-powered healthcare.
1.The Role of IoT in Modern Hospitals
IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices that collect, share, and analyze data in real time. In hospitals, IoT enables continuous monitoring of patients, automation of routine tasks, and optimized resource management. By integrating IoT-enabled devices with hospital management systems, healthcare institutions can achieve improved patient outcomes, reduced operational costs, and enhanced safety standards.
2. Key Benefits of IoT in Hospitals
2.1 Improved Patient Outcomes
The ultimate goal of healthcare is to deliver better patient outcomes, and IoT is making this easier than ever. By providing real-time data on patient health, IoT enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions quickly. For example:
- Wearable devices can monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, alerting doctors to abnormalities before they become critical.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) integrated with IoT devices ensure that patient data is always up-to-date and accessible, reducing the risk of errors and improving treatment accuracy.
2.2 Enhanced Patient Safety
IoT is a game-changer for patient safety. Here’s how:
- Real-time monitoring: IoT sensors can track patients’ conditions 24/7, reducing the risk of adverse events.
- Location-based tracking: IoT-enabled devices can monitor the movement of patients, especially those with dementia or other conditions, ensuring they don’t wander into unsafe areas.
- Contact tracing: During pandemics like COVID-19, IoT can track interactions between patients and staff, helping to contain outbreaks.
2.3 Increased Operational Efficiency
Hospitals are complex environments with countless moving parts. IoT simplifies operations by:
- Automating routine tasks: For example, IoT sensors can monitor medical equipment like infusion pumps and ventilators, alerting staff when maintenance is needed.
- Streamlining workflows: IoT can track the location of medical equipment, reducing the time staff spend searching for it.
- Optimizing inventory management: IoT sensors can monitor supply levels and automatically reorder items when stocks run low, reducing waste and ensuring availability.
2.4 Remote Patient Monitoring
IoT enables hospitals to extend care beyond their walls. With remote monitoring, patients can recover in the comfort of their homes while still being closely watched by healthcare providers. This not only improves patient satisfaction but also reduces hospital readmissions and frees up beds for critical cases.
2.5 Cost Reduction
By automating processes and improving efficiency, IoT helps hospitals save money. For instance:
- Predictive maintenance: IoT can predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing hospitals to schedule repairs before a breakdown occurs.
- Reduced waste: Automated inventory management ensures that supplies are used efficiently, minimizing overstocking and waste.
3.Enhanced Patient Outcomes with Real-Time Monitoring
IoT enables continuous, real-time patient monitoring, ensuring early detection of critical health conditions. Hospitals in the U.S. and Europe are already leveraging IoT-powered wearable devices to monitor:
- Vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- Post-operative recovery, allowing doctors to track healing progress remotely.
- Chronic disease management, particularly for conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
In India, remote monitoring has been a breakthrough in rural healthcare, where access to specialists is limited. Patients can weIntroduction
The healthcare industry is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by advancements in technology. Among these, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a game-changer, transforming hospital operations and patient care. Hospitals across the globe, from the United States to the United Kingdom, Australia, and India, are integrating IoT-driven solutions to enhance patient outcomes, streamline processes, and improve overall efficiency.
For hospital administrators, doctors, and decision-makers, understanding the significance of IoT is no longer optional—it is essential for staying competitive and delivering high-quality care. This article explores the role of IoT in modern hospitals, its key applications, benefits, challenges, and the future of IoT-powered healthcare.
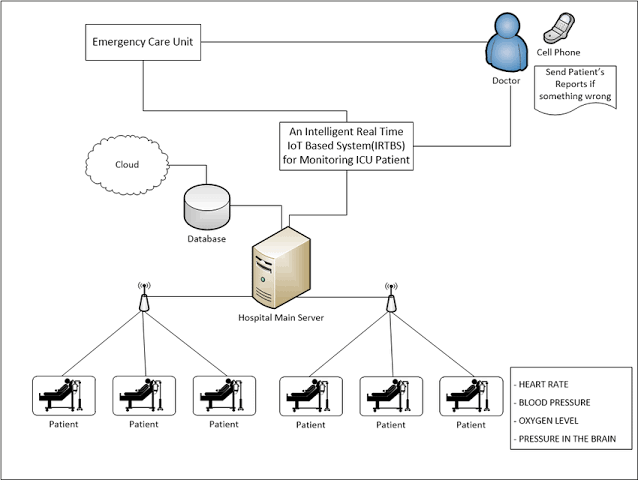
- IoT sensors can provide reliable data on patients’ conditions, vital signs, and other health-related indicators in real time.
- Healthcare practitioners can analyse this data to make educated decisions about patient care.
- For example, IoT-enabled devices can monitor a patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs and alert healthcare professionals if there are any abnormalities, which can help to prevent adverse events.
4.The Role of IoT in Modern Hospitals
IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices that collect, share, and analyze data in real time. In hospitals, IoT enables continuous monitoring of patients, automation of routine tasks, and optimized resource management. By integrating IoT-enabled devices with hospital management systems, healthcare institutions can achieve improved patient outcomes, reduced operational costs, and enhanced safety standards.
5.IoT-enabled devices that transmit data directly to doctors in urban hospitals.
1. Improved Patient Safety and Infection Control
Hospitals in Australia and the UK are implementing IoT-based systems for:
- Fall detection: Sensors alert nurses if elderly or high-risk patients attempt to move unsupervised.
- Location tracking: IoT devices track the movement of patients with cognitive impairments to prevent wandering into unsafe areas.
- Infection control: IoT sensors monitor hand hygiene compliance among healthcare staff, reducing hospital-acquired infections.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, IoT-enabled contact tracing systems helped hospitals worldwide track interactions between patients and staff, preventing the spread of infections.
2. Optimized Operational Efficiency
IoT automates various hospital operations, improving workflow and reducing human error. Key applications include:
- Smart inventory management: IoT sensors monitor medical supplies and automatically place orders when stocks are low.
- Equipment tracking: In large hospitals, IoT-powered RFID tags prevent the loss of critical medical devices such as ventilators and infusion pumps.
- Automated maintenance alerts: IoT detects early signs of equipment failure, reducing downtime and costly emergency repairs.
3. Remote Patient Monitoring and Telemedicine
IoT is bridging the gap between hospitals and patients, especially in remote areas. Hospitals in the U.S. and UK use IoT-powered telemedicine solutions for:
- Virtual consultations, reducing unnecessary hospital visits.
- Home-based monitoring, allowing elderly patients to receive care without hospitalization.
- Post-surgical follow-ups, ensuring faster recovery while freeing up hospital beds.
India’s Apollo Hospitals has implemented IoT-powered health kiosks in rural regions, allowing villagers to undergo basic health check-ups remotely.
4. Cost Reduction and Financial Efficiency
Hospitals worldwide are witnessing significant cost savings through IoT adoption. Examples include:
- Predictive maintenance: IoT helps hospitals predict when medical equipment will fail, reducing expensive breakdowns.
- Efficient resource allocation: IoT-based tracking ensures optimal utilization of medical staff and infrastructure.
- Reduction in hospital readmissions: Continuous patient monitoring prevents complications, leading to fewer re-hospitalizations.
6.Global Adoption of IoT in Healthcare
United States
The U.S. leads IoT healthcare adoption, with hospitals integrating AI-powered diagnostics and remote monitoring systems. The Mayo Clinic and Cleveland Clinic have successfully implemented IoT for AI-driven patient analysis and predictive healthcare models.
United Kingdom
The National Health Service (NHS) is leveraging IoT for smart hospitals. IoT-powered medication adherence systems remind patients to take prescribed medicines, reducing emergency admissions.
Australia
Australian hospitals use IoT for real-time bed occupancy monitoring, reducing patient wait times in emergency departments. Wearable devices are also improving elderly care in aged-care facilities.
India
IoT adoption in India focuses on bridging the urban-rural healthcare divide. Initiatives like AIIMS’ IoT-based health monitoring projects are revolutionizing diagnostics in remote villages.
7.Challenges of Implementing IoT in Hospitals
While IoT offers immense potential, its implementation comes with challenges:
1. Data Security and Privacy Risks
IoT devices collect and transmit sensitive patient data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Hospitals must invest in:
- End-to-end encryption to protect data integrity.
- Multi-factor authentication to restrict unauthorized access.
- Regular cybersecurity audits to identify vulnerabilities.
2. Interoperability Issues
Hospitals use devices from different manufacturers, often leading to compatibility challenges. Standardized IoT protocols are essential to ensure seamless communication between systems.
3. High Initial Investment
IoT implementation requires substantial capital investment in devices, infrastructure, and staff training. However, the long-term savings outweigh initial costs.
4. Managing Data Overload
IoT generates vast amounts of data, which can overwhelm healthcare providers. AI-driven analytics tools can help derive actionable insights from this data.
8.The Future of IoT in Hospitals
The next phase of IoT in healthcare will include:
- AI-powered diagnostics, improving early disease detection.
- Smart hospitals, where IoT manages everything from patient care to energy consumption.
- Personalized medicine, where IoT data enables customized treatments based on genetic profiles.
9.Why Hospitals Must Embrace IoT Now
The global healthcare landscape is evolving rapidly. Hospitals that fail to integrate IoT will struggle to compete with smarter, more efficient institutions. The time to invest in IoT is now, ensuring better patient care, reduced costs, and enhanced hospital management.
Why Hospitals Must Embrace IoT Now
For hospital administrators and decision-makers, the question isn’t whether to adopt IoT—it’s when. The benefits of IoT, from improved patient outcomes to cost savings, are too significant to ignore. By investing in IoT-enabled hospital management software, hospitals can stay ahead of the curve and deliver better care in an increasingly competitive healthcare landscape.
Enhanced Data Analysis
Contact Tracing
- The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for contact tracing in hospitals.
- IoT-enabled devices can be used to track the movement of staff and patients, enabling hospitals to quickly identify and isolate potential COVID-19 cases.
- This can help to prevent the spread of the virus within the hospital.
- In conclusion, IoT has transformed the healthcare industry by enhancing safety in hospitals.
- With real-time patient monitoring, location-based tracking, improved staff safety, enhanced security, and contact tracing, hospitals can ensure that patients and staff are safe at all times.
- The implementation of IoT technology in hospitals is a significant step forward in the healthcare industry’s efforts to provide safe and efficient patient care.
- As IoT technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovations that will help hospitals enhance safety and provide better patient care.
Final Thoughts
The Internet of Things is not a futuristic concept—it is already transforming hospitals worldwide. From real-time patient monitoring to seamless operational efficiency, IoT is enhancing every aspect of healthcare. Despite challenges, its benefits far outweigh the risks, making IoT an indispensable tool for modern hospitals.
By adopting IoT, hospitals can unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, safety, and patient satisfaction, paving the way for a brighter future in global healthcare.
For more insights on cutting-edge healthcare technologies, visit: Hospi.info/blog
FAQs:
Q: What is IoT in healthcare, and how is it transforming hospitals?
A: The Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare refers to the integration of connected devices and smart technology to improve patient care and hospital efficiency. IoT enables real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven decision-making. Hospitals leverage IoT for remote patient monitoring, automated medication tracking, predictive maintenance of medical equipment, and improved hospital workflow. By reducing human errors, enhancing patient safety, and optimizing resource allocation, IoT is revolutionizing modern healthcare facilities.
Q: How does IoT improve patient care in hospitals?
A: IoT enhances patient care through real-time monitoring, wearable health devices, and AI-powered analytics. Smart sensors track vital signs and alert doctors to any abnormalities, enabling early intervention. IoT-enabled hospital beds adjust automatically for patient comfort, while connected medical devices ensure timely medication administration. Remote monitoring allows physicians to oversee patients’ health even outside the hospital, reducing readmissions and improving treatment outcomes.
Q: What are the key benefits of IoT in hospital operations?
A: IoT optimizes hospital operations by reducing manual work, automating administrative tasks, and enhancing asset management. It streamlines patient flow, improves inventory tracking for medications and medical supplies, and enhances predictive maintenance for hospital equipment. IoT-powered analytics provide insights for better decision-making, resulting in cost savings, improved efficiency, and a better patient experience.
Q: How does IoT help with remote patient monitoring?
A: Remote patient monitoring (RPM) uses IoT devices like wearables, smartwatches, and connected sensors to track a patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, oxygen levels, and blood pressure, in real-time. This data is transmitted to healthcare providers, allowing them to detect early signs of deterioration and take preventive action. RPM reduces hospital readmissions, enables home-based care, and ensures continuous patient monitoring without requiring frequent hospital visits.
Q: What are some real-world examples of IoT in hospitals?
A: Many hospitals worldwide have successfully integrated IoT solutions. For example, Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York uses IoT to optimize patient flow and reduce wait times. The Cleveland Clinic employs remote patient monitoring to track post-surgery patients. Smart hospital beds in hospitals across Europe automatically adjust based on patient movements, improving comfort and reducing the risk of bedsores. These implementations show how IoT is enhancing healthcare efficiency and patient outcomes.
Q: How does IoT improve hospital security and patient safety?
A: IoT improves security and safety by using smart surveillance cameras, biometric access controls, and RFID-based patient tracking. Connected security systems monitor hospital premises 24/7, while IoT-enabled wristbands help track patients, preventing newborn mix-ups or unauthorized patient exits. Additionally, IoT-powered medication tracking systems ensure the right drugs are administered at the correct time, reducing errors and enhancing patient safety.
Q: What role does IoT play in predictive maintenance of hospital equipment?
A: IoT helps hospitals maintain their medical equipment proactively. Sensors embedded in medical devices collect performance data and predict failures before they occur. This allows hospitals to schedule maintenance in advance, preventing equipment downtime. Predictive maintenance improves the longevity of expensive medical machines, reduces emergency repair costs, and ensures uninterrupted patient care.
Q: How does IoT support infection control in hospitals?
A: IoT assists infection control by monitoring hand hygiene compliance, tracking air quality, and automating cleaning processes. Smart dispensers ensure healthcare staff follow handwashing protocols, while environmental sensors detect contamination risks. IoT-enabled robots sanitize hospital rooms using UV light, reducing the spread of infections and enhancing hospital hygiene.
Q: What impact does IoT have on hospital cost savings?
A: IoT helps hospitals cut costs by reducing manual errors, optimizing resource utilization, and preventing equipment failures. Automated inventory management reduces waste, while energy-efficient IoT systems lower electricity bills. Real-time data analytics help hospitals make informed financial decisions, ultimately reducing operational expenses and improving profitability.
Q: How is IoT used in emergency care and ambulance services?
A: IoT enhances emergency care by equipping ambulances with smart medical devices that transmit real-time patient data to hospitals before arrival. Paramedics use connected ECG monitors and wearable sensors to track vital signs, enabling doctors to prepare for immediate treatment. GPS tracking ensures faster ambulance dispatch, improving response times in critical situations.
Q: What are the challenges of implementing IoT in hospitals?
A: While IoT offers many benefits, hospitals face challenges such as data security risks, high implementation costs, and interoperability issues between different devices. Ensuring HIPAA compliance, maintaining network security, and training healthcare staff on IoT technology are also critical hurdles. However, with proper cybersecurity measures and strategic planning, these challenges can be managed effectively.
Q: How does IoT help in medication management?
A: IoT-enabled smart medication dispensers and RFID tracking systems ensure accurate drug administration and inventory control. These systems alert nurses and pharmacists when medication levels are low or when a patient misses a dose, reducing prescription errors and improving patient adherence to treatment plans.
Q: What is the role of AI in IoT-powered hospitals?
A: Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhances IoT capabilities by analyzing vast amounts of patient data to provide predictive insights. AI-powered analytics help doctors detect diseases early, optimize hospital resource allocation, and personalize treatment plans. Machine learning algorithms improve decision-making, making IoT-based healthcare systems smarter and more efficient.
Q: How does IoT contribute to smart hospital infrastructure?
A: IoT enables smart hospital buildings by integrating connected HVAC systems, automated lighting, and energy-efficient operations. Smart climate control ensures patient comfort, while IoT sensors adjust lighting and temperature based on occupancy. This creates a sustainable hospital environment while reducing energy costs.
Q: How does IoT improve hospital workflow management?
A: IoT streamlines hospital workflows by automating patient check-ins, scheduling appointments, and optimizing staff assignments. Connected systems analyze patient flow patterns to reduce bottlenecks in emergency rooms and waiting areas. This leads to faster service, reduced wait times, and better patient satisfaction.
Q: How secure is patient data in IoT-enabled hospitals?
A: IoT security in hospitals is a major concern, but advanced encryption protocols, blockchain technology, and multi-factor authentication help protect patient data. Hospitals must follow strict data privacy regulations like HIPAA and GDPR to safeguard sensitive medical information from cyber threats.
Q: How can hospitals implement IoT without disrupting existing systems?
A: Hospitals can adopt IoT in phases, starting with pilot programs in specific departments. Integrating IoT with existing electronic health records (EHR) and training staff ensures a smooth transition. Partnering with IoT vendors that offer interoperability solutions also helps in seamless adoption.
Q: How will IoT shape the future of healthcare?
A: IoT will continue to revolutionize healthcare by enabling AI-driven diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and remote surgeries using robotic technology. As 5G networks expand, IoT devices will become even more efficient, offering faster real-time data processing and enhancing global healthcare accessibility.
Q: How does IoT improve patient engagement and experience in hospitals?
A: IoT enhances patient engagement by providing real-time health updates, interactive hospital apps, and personalized care. Patients can use wearable devices to monitor their health, receive medication reminders, and communicate with doctors remotely. Smart hospital rooms allow patients to control lighting, temperature, and entertainment systems using voice commands or mobile apps, making their hospital stay more comfortable and stress-free.
Q: What role does IoT play in telemedicine?
A: IoT is a key enabler of telemedicine, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely and provide virtual consultations. Wearable health devices, smart diagnostic tools, and real-time data sharing improve the accuracy of remote diagnoses. IoT-based video conferencing and AI-powered chatbots enhance doctor-patient interactions, reducing the need for in-person visits while ensuring timely medical assistance.
Q: How does IoT assist in elderly care and assisted living?
A: IoT devices such as smart fall detectors, GPS trackers, and AI-powered voice assistants help elderly patients live independently while ensuring their safety. Smart home sensors monitor activity levels, detect emergencies, and send alerts to caregivers or family members. Wearable devices track vital signs and medication adherence, improving elderly care management and reducing hospitalization risks.
Q: How does IoT help in tracking hospital assets and medical supplies?
A: IoT-enabled RFID tags and GPS trackers help hospitals monitor the location and usage of medical equipment, ensuring efficient asset management. Smart inventory systems track medication stock levels in real time, preventing shortages or overstocking. Automated alerts notify staff when equipment needs maintenance, reducing downtime and operational delays.
Q: What are the privacy concerns associated with IoT in hospitals?
A: Privacy concerns in IoT-enabled hospitals include unauthorized access to patient data, data breaches, and cyberattacks. To mitigate these risks, hospitals must implement strong encryption, access control policies, and regular security audits. Compliance with data protection regulations like HIPAA and GDPR ensures that patient information remains confidential and secure.
Q: How can hospitals ensure seamless integration of IoT devices?
A: Hospitals should adopt standardized protocols for device interoperability, use cloud-based IoT platforms, and collaborate with technology providers. Training healthcare professionals on IoT usage and cybersecurity best practices is essential for successful integration. Partnering with IoT vendors that offer scalable and secure solutions ensures smooth implementation and long-term reliability.
Q: How does IoT help in reducing hospital-acquired infections (HAIs)?
A: IoT-powered solutions, such as automated hand hygiene monitoring, UV disinfection robots, and smart air filtration systems, help minimize hospital-acquired infections. Wearable biosensors detect early infection signs in patients, while AI-driven analytics identify infection hotspots, allowing hospitals to take preventive measures. These technologies significantly reduce infection rates and improve patient safety.
Q: What are some leading IoT healthcare solutions used globally?
A: Some of the top IoT healthcare solutions include remote patient monitoring platforms like BioIntelliSense and Philips IntelliVue, smart hospital management systems like GE Healthcare’s Command Center, and AI-driven diagnostic tools such as IBM Watson Health. These solutions help hospitals improve patient care, streamline operations, and enhance data-driven decision-making.
Q: How does IoT contribute to reducing emergency room (ER) overcrowding?
A: IoT helps optimize emergency room operations by providing real-time data on patient wait times, bed availability, and resource allocation. AI-powered predictive analytics forecast ER demand, enabling hospitals to prepare in advance. Wearable devices track patient conditions, allowing doctors to prioritize critical cases efficiently, thereby reducing ER congestion and improving patient outcomes.
Q: How do hospitals use IoT for real-time health monitoring?
A: Hospitals use IoT-powered wearable devices, biosensors, and connected monitors to track patients’ vital signs continuously. These devices collect data on heart rate, oxygen levels, glucose levels, and more, providing real-time updates to healthcare providers. If abnormalities are detected, alerts are sent to doctors, enabling quick intervention and reducing medical emergencies.
Q: How does IoT impact hospital staffing and workforce management?
A: IoT-driven workforce management tools help hospitals optimize staff scheduling, track employee performance, and improve workflow efficiency. Smart badge systems monitor staff movement, ensuring optimal resource allocation. AI-powered predictive models help hospitals forecast staffing needs, reducing burnout and improving overall productivity.
Q: How can hospitals use IoT for personalized patient care?
A: IoT enables personalized healthcare by analyzing patient-specific data and tailoring treatment plans accordingly. Smart wearables track individual health metrics, allowing doctors to recommend personalized medications and lifestyle changes. AI-driven chatbots provide patients with customized health tips, improving engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
Q: What is the future of IoT in hospital management?
A: The future of IoT in hospital management includes AI-powered automation, blockchain-based patient data security, and 5G-enabled smart devices for ultra-fast real-time monitoring. Hospitals will leverage digital twins—virtual replicas of physical hospital environments—to simulate and optimize operations. These advancements will lead to more efficient, patient-centric healthcare systems.
Q: How does IoT help in mental health monitoring?
A: IoT-powered mental health apps and wearable devices track sleep patterns, stress levels, and emotional responses using biosensors and AI analytics. Smart chatbots provide real-time support, while connected therapy tools enable remote counseling. These solutions help individuals manage stress, anxiety, and depression while providing valuable data for mental health professionals.
Q: What role does 5G play in IoT-driven hospitals?
A: 5G enhances IoT-powered hospitals by providing ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity for real-time data exchange. It enables seamless telemedicine consultations, high-speed medical imaging, and uninterrupted remote patient monitoring. With 5G, hospitals can deploy more IoT devices without network congestion, improving overall healthcare efficiency.
Q: How does IoT contribute to reducing medical errors?
A: IoT reduces medical errors by automating processes such as medication administration, patient identification, and diagnostic procedures. Smart medication dispensers ensure accurate dosages, while RFID-based tracking prevents surgical errors. AI-driven decision support systems analyze patient data to detect potential risks, improving clinical accuracy.
Q: Can IoT help in managing chronic diseases?
A: Yes, IoT is highly effective in managing chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Wearable health monitors continuously track patient vitals and alert doctors to any concerning trends. AI-driven predictive models analyze health patterns, helping doctors recommend proactive treatment strategies and lifestyle changes.
Q: What industries are investing in IoT-driven hospital solutions?
A: Leading tech companies such as Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are investing in IoT healthcare solutions. MedTech giants like Philips, GE Healthcare, and Siemens are developing smart medical devices and AI-driven hospital management platforms. These investments are accelerating IoT adoption in hospitals worldwide.
Q: How does IoT impact hospital sustainability?
A: IoT helps hospitals achieve sustainability goals by reducing energy consumption, minimizing medical waste, and optimizing water usage. Smart energy management systems adjust lighting and temperature based on occupancy, while AI-driven analytics help hospitals implement eco-friendly waste disposal methods. These innovations contribute to a greener healthcare environment.
Q: How can small hospitals afford IoT implementation?
A: Small hospitals can start with cost-effective IoT solutions like cloud-based remote monitoring, AI-powered diagnostic tools, and smart inventory tracking. Many IoT vendors offer scalable subscription-based models, reducing upfront costs. Government grants and healthcare innovation programs also support small hospitals in adopting IoT technology.
Q: What are the regulatory challenges of IoT adoption in healthcare?
A: Regulatory challenges include compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other data protection laws. Hospitals must ensure IoT devices meet cybersecurity standards, undergo regular audits, and obtain regulatory approvals before deployment. Governments are working to establish standardized guidelines to facilitate secure and ethical IoT adoption in healthcare.
Q: How does IoT enable real-time ambulance tracking?
A: IoT-powered GPS tracking systems allow hospitals to monitor ambulance locations in real time. Integrated communication platforms provide paramedics with instant access to patient medical records, enabling better pre-hospital care. AI-powered traffic analytics optimize ambulance routes, reducing response times in emergencies.
Q: How does IoT transform neonatal and maternity care?
A: IoT improves neonatal care by providing real-time monitoring of premature babies using smart incubators and biosensors. IoT-enabled maternity apps help pregnant women track fetal development and receive timely medical advice. AI-driven analytics detect early signs of complications, ensuring better maternal and infant health outcomes.
Want a quick walkthrough of Hospi?
We offer gentle, no-pressure demos for hospitals, labs & clinics.
Or call us directly: +91 8179508852


